JoF | Free Full-Text | Lipid Species in the GI Tract are Increased by the Commensal Fungus Candida albicans and Decrease the Virulence of Clostridioides difficile | HTML

Prognostic factors for severe and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: a systematic review - ScienceDirect

Extended-pulsed fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection in patients 60 years and older (EXTEND): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3b/4 trial - The Lancet Infectious Diseases

A population-based spatio-temporal analysis of Clostridium difficile infection in Queensland, Australia over a 10-year period - Journal of Infection

A population-based spatio-temporal analysis of Clostridium difficile infection in Queensland, Australia over a 10-year period - Journal of Infection
Extended-pulsed fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection in patients 60 years and older (EXTEND): a ran
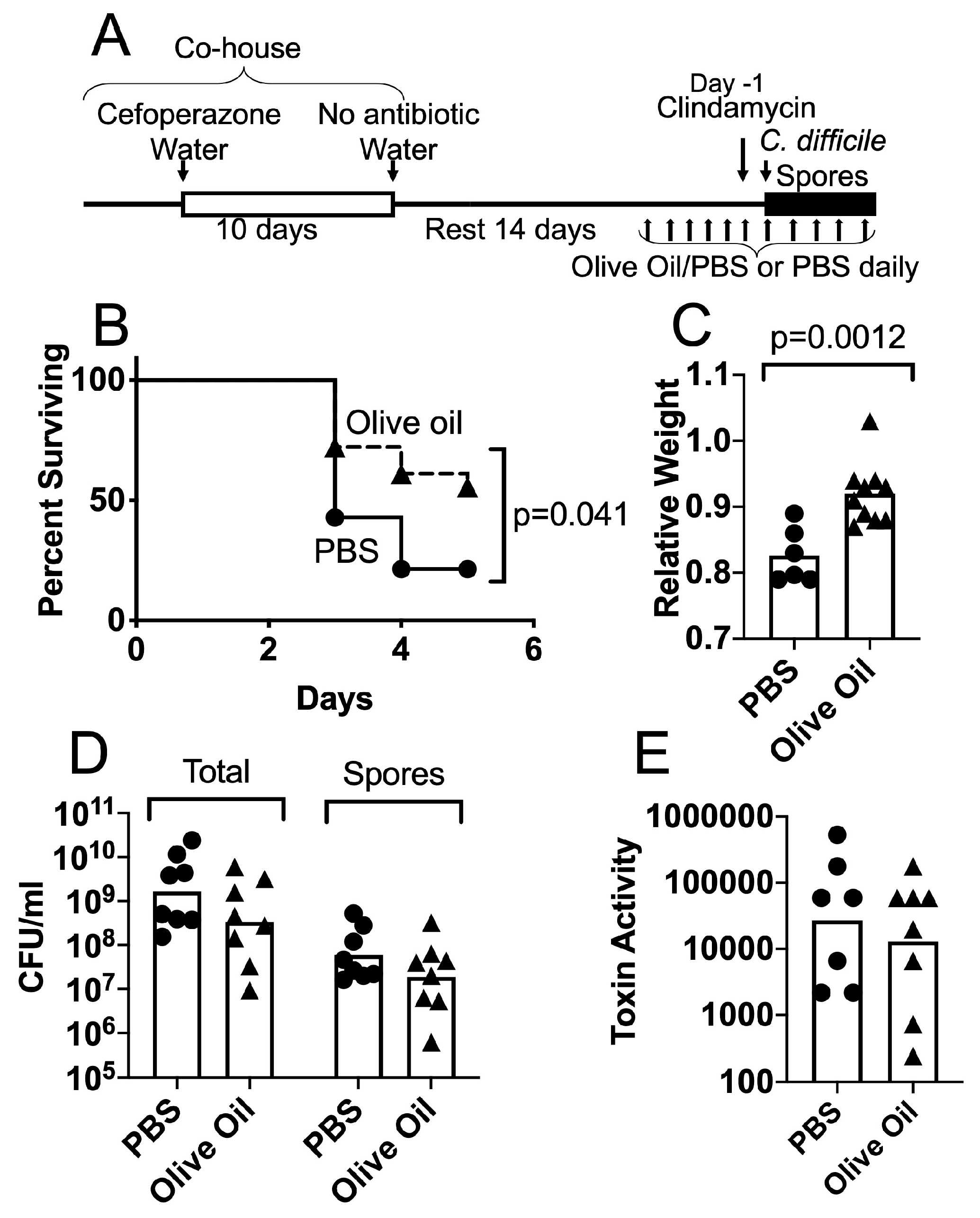
JoF | Free Full-Text | Lipid Species in the GI Tract are Increased by the Commensal Fungus Candida albicans and Decrease the Virulence of Clostridioides difficile | HTML

Patient disposition. CDAD = C. difficile-associated diarrhea; mITT =... | Download Scientific Diagram

Prognostic factors for severe and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection: a systematic review - ScienceDirect

Extended-pulsed fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection in patients 60 years and older (EXTEND): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3b/4 trial - The Lancet Infectious Diseases
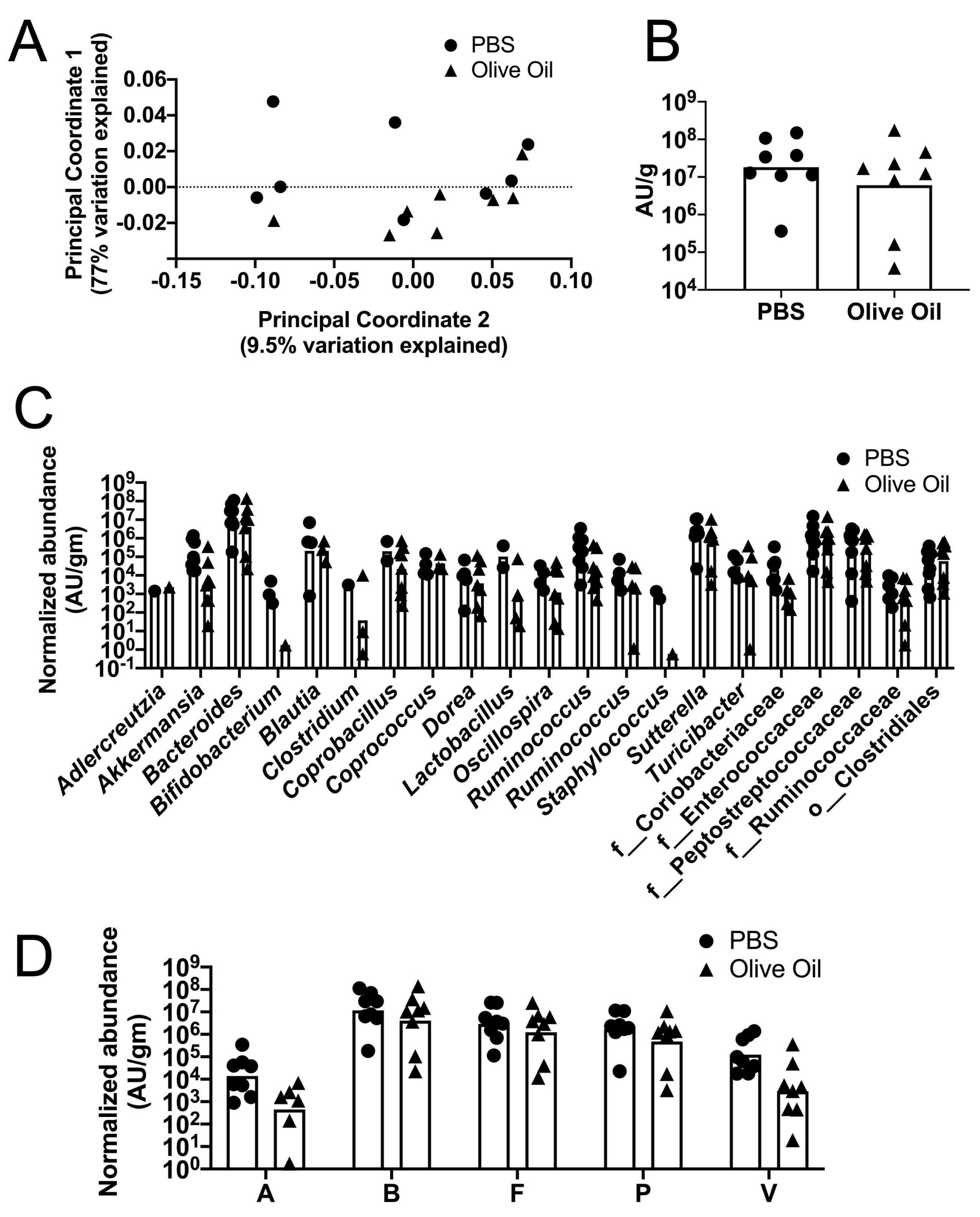
JoF | Free Full-Text | Lipid Species in the GI Tract are Increased by the Commensal Fungus Candida albicans and Decrease the Virulence of Clostridioides difficile | HTML
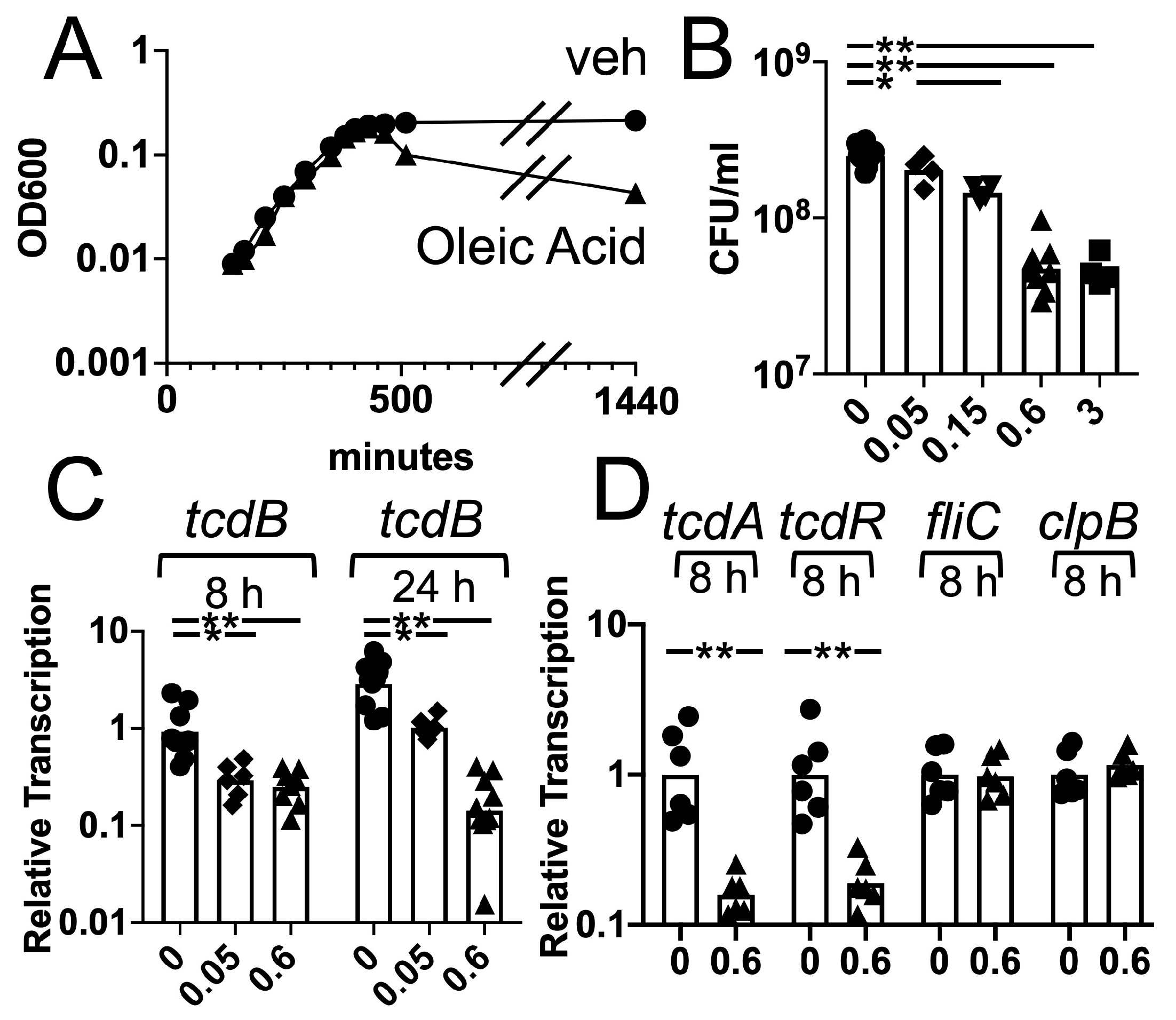
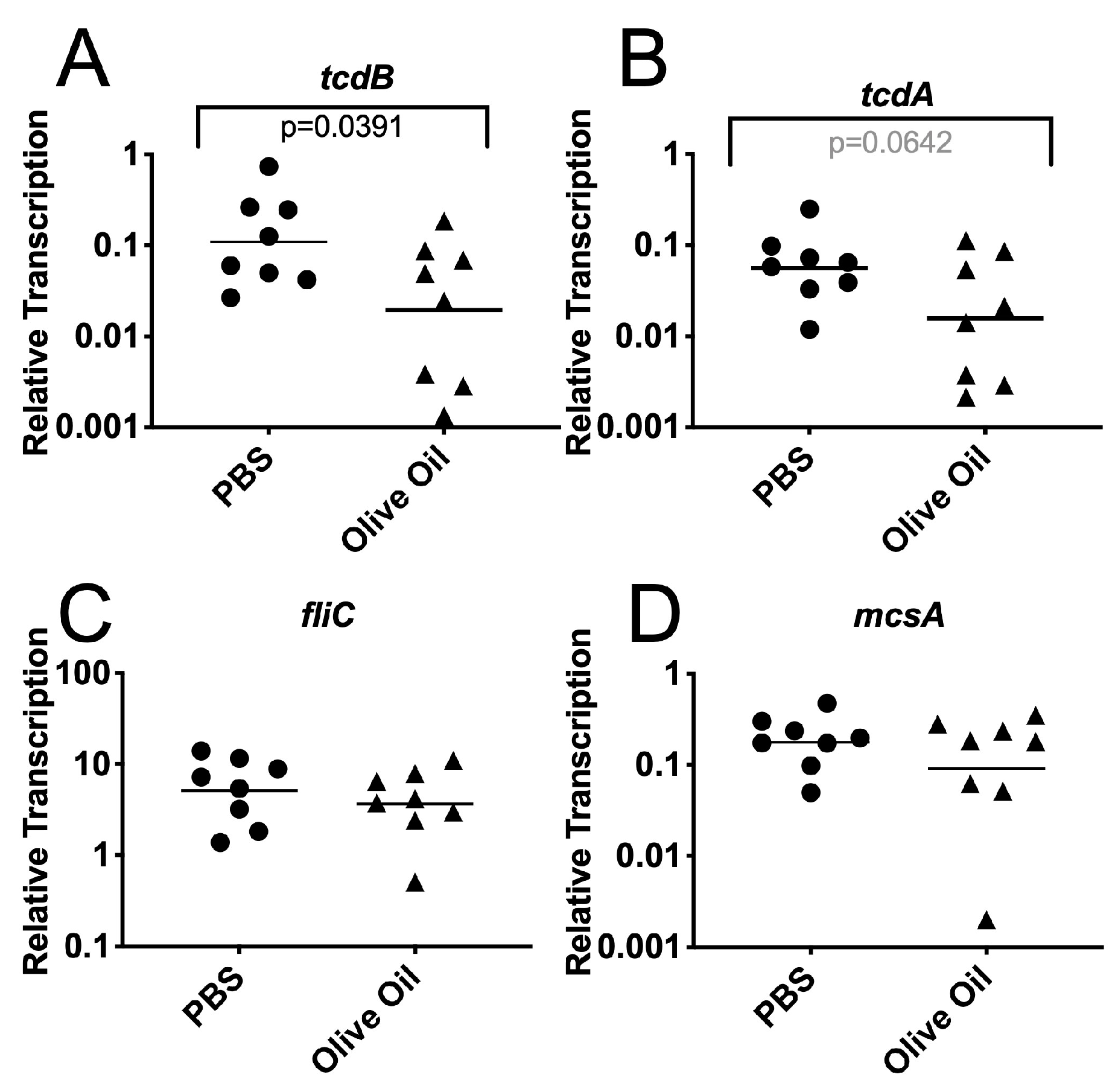
JoF | Free Full-Text | Lipid Species in the GI Tract are Increased by the Commensal Fungus Candida albicans and Decrease the Virulence of Clostridioides difficile | HTML

Growth (a) and toxin levels (b and c) for C. difficile strain UK-14 (an... | Download Scientific Diagram
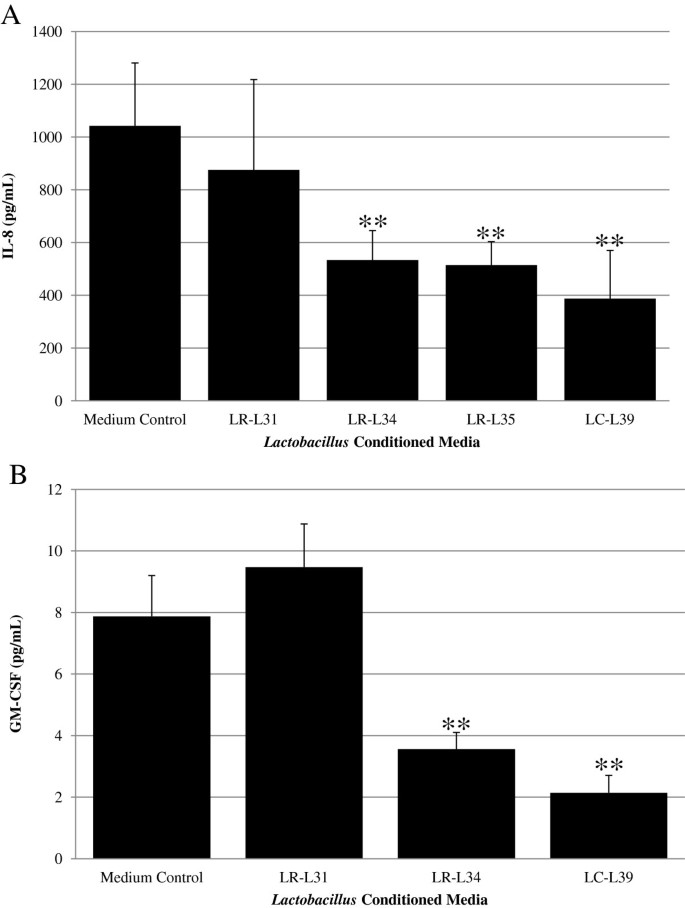
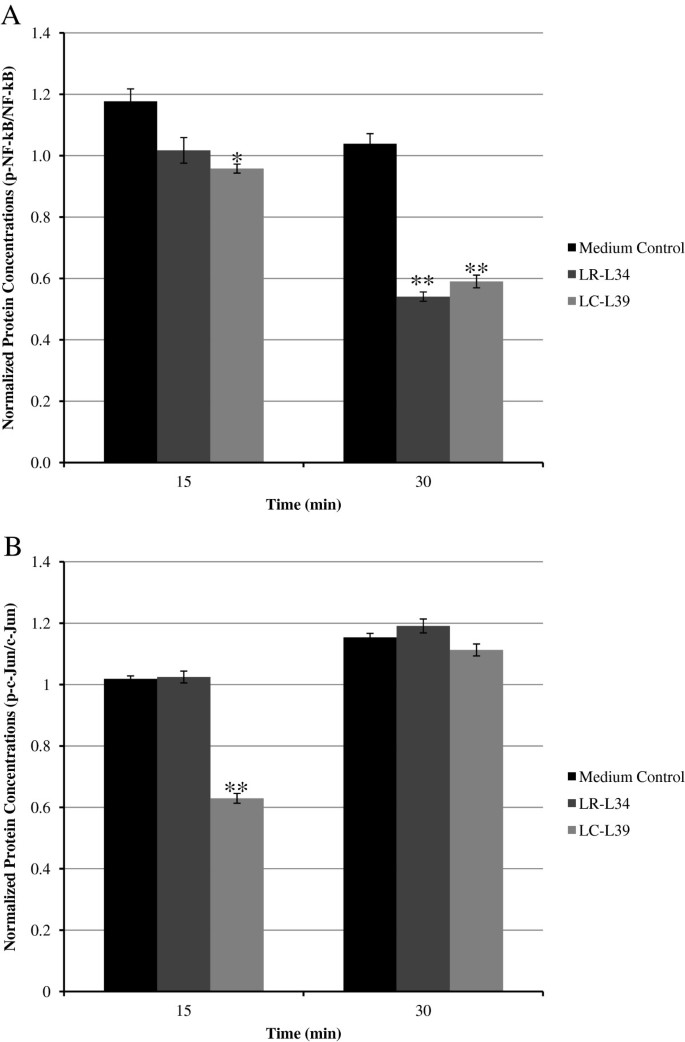
Lactobacillus rhamnosus L34 and Lactobacillus casei L39 suppress Clostridium difficile-induced IL-8 production by colonic epithelial cells | BMC Microbiology | Full Text
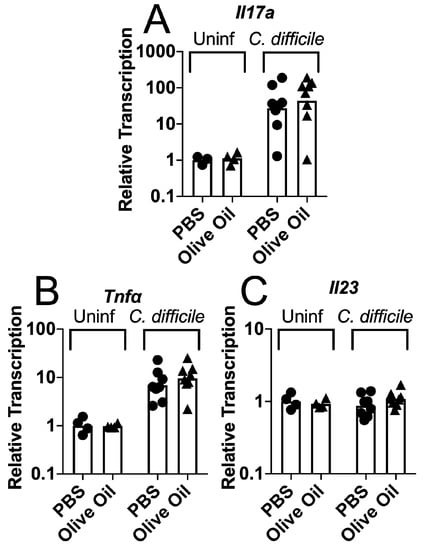
JoF | Free Full-Text | Lipid Species in the GI Tract are Increased by the Commensal Fungus Candida albicans and Decrease the Virulence of Clostridioides difficile | HTML
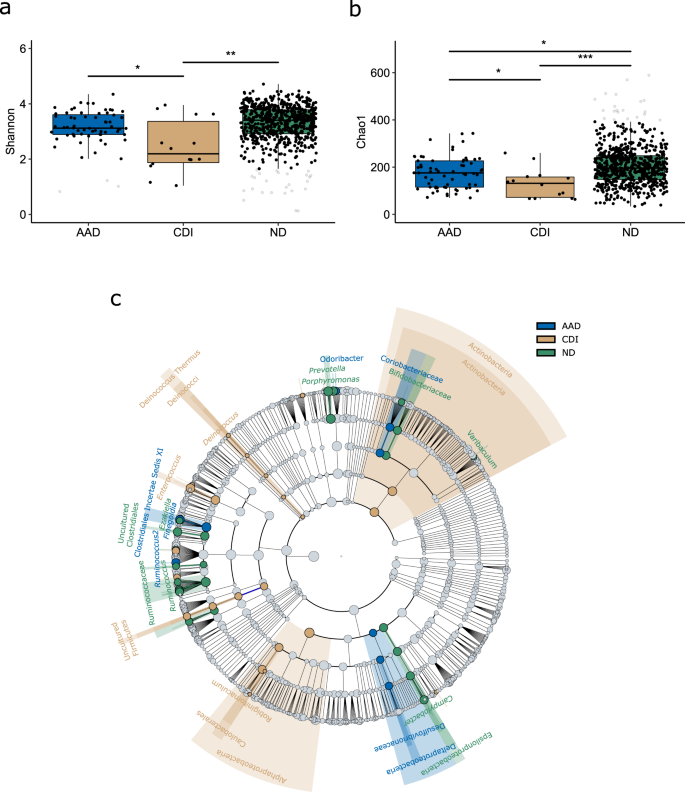
Microbiota-based markers predictive of development of Clostridioides difficile infection | Nature Communications
A population-based spatio-temporal analysis of Clostridium difficile infection in Queensland, Australia over a 10-year period

Novel risk factors for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection in children. - Abstract - Europe PMC

European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: 2021 update on the treatment guidance document for Clostridioides difficile infection in adults - Clinical Microbiology and Infection
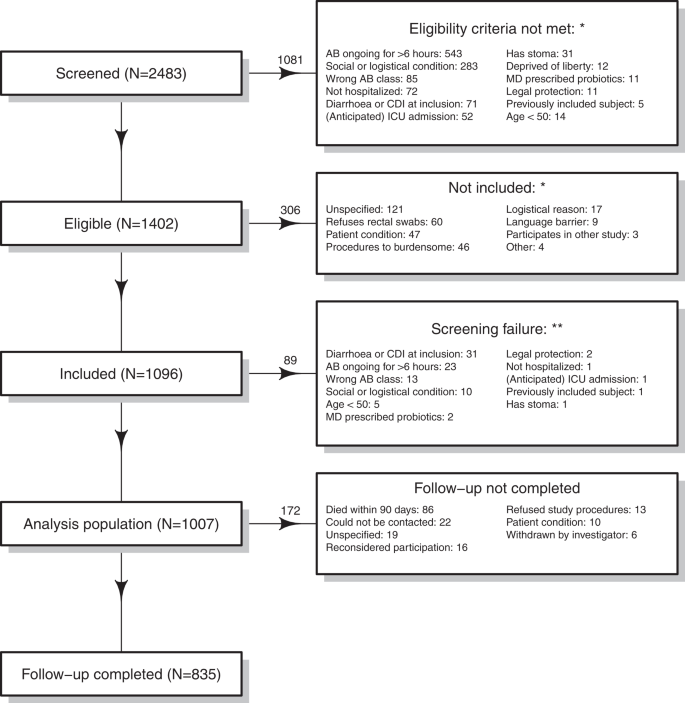
Incidence and predictive biomarkers of Clostridioides difficile infection in hospitalized patients receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics | Nature Communications

Microbiota-based markers predictive of development of Clostridioides difficile infection | Nature Communications