Frontiers | The T-Type Calcium Channel Cav3.2 in Somatostatin Interneurons in Spinal Dorsal Horn Participates in Mechanosensation and Mechanical Allodynia in Mice

VGLUT3 is expressed by a unique subset of small- and medium-sized DRG... | Download High-Resolution Scientific Diagram

Functional Reorganization of Local Circuit Connectivity in Superficial Spinal Dorsal Horn with Neuropathic Pain States | eNeuro

The histology, physiology, neurochemistry and circuitry of the substantia gelatinosa Rolandi (lamina II) in mammalian spinal cord - ScienceDirect
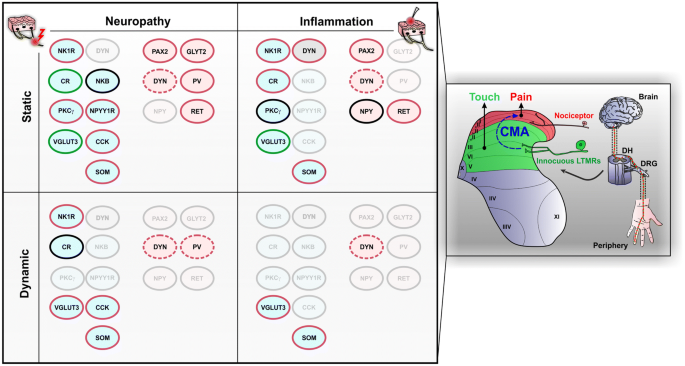
Recent advances in our understanding of the organization of dorsal horn neuron populations and their contribution to cutaneous mechanical allodynia | SpringerLink

Mechanical Allodynia Circuitry in the Dorsal Horn Is Defined by the Nature of the Injury - ScienceDirect
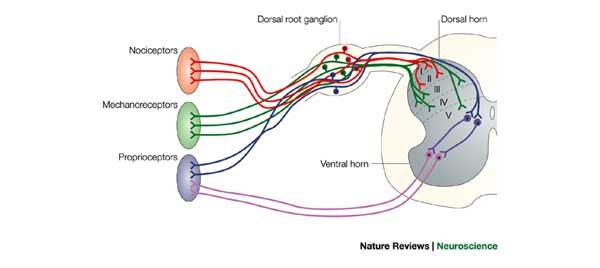
Patterning cell types in the dorsal spinal cord: what the mouse mutants say | Nature Reviews Neuroscience

Distinct Populations of Spinal Cord Lamina II Interneurons Expressing G-Protein-Gated Potassium Channels | Journal of Neuroscience

Novel inhibitory brainstem neurons with selective projections to spinal lamina I reduce both pain and itch - Agostinelli - 2021 - Journal of Comparative Neurology - Wiley Online Library

Specific gene expression in unmyelinated dorsal root ganglion neurons in nonhuman primates by intra-nerve injection of AAV 6 vector: Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development
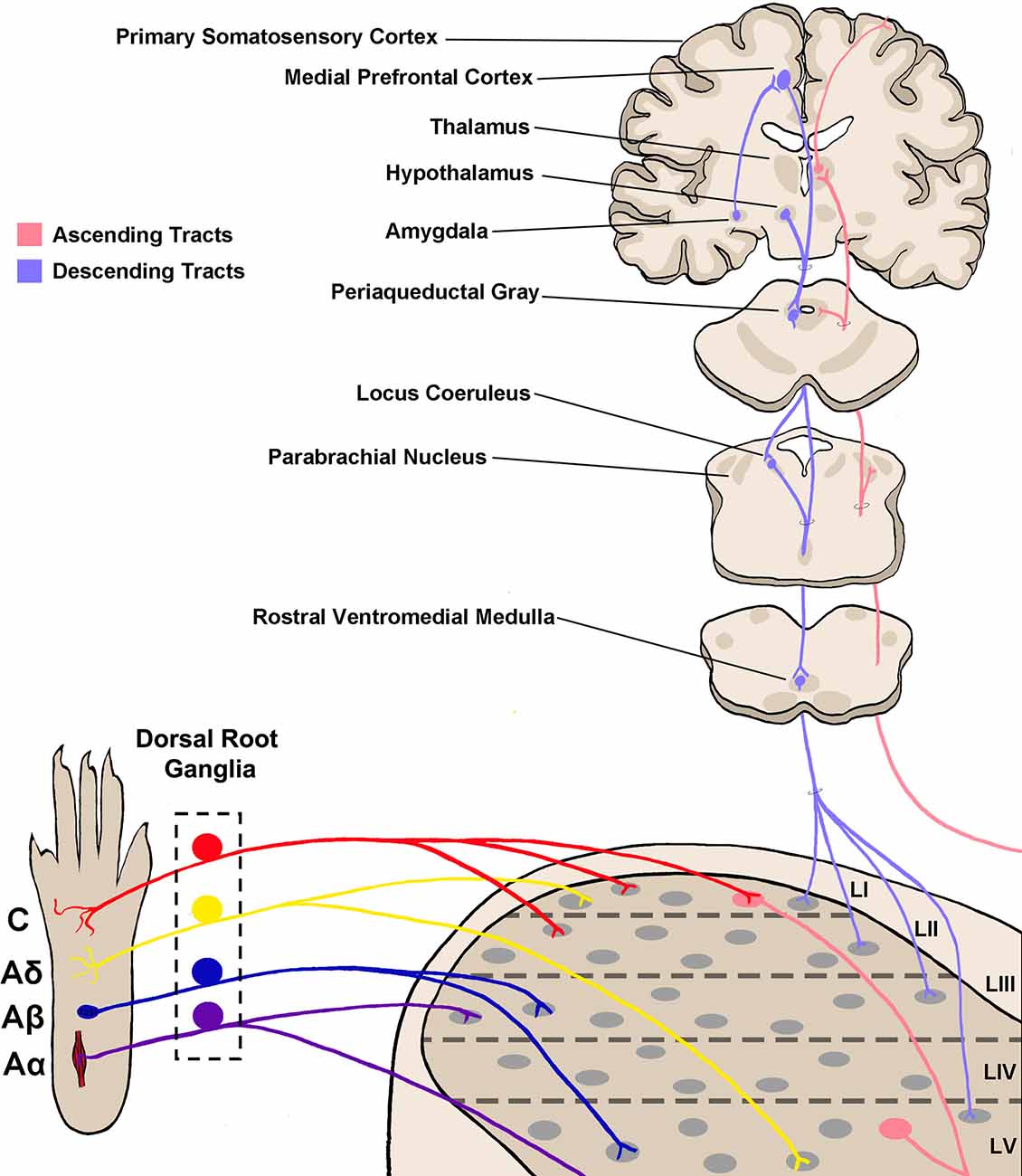
Frontiers | Insights Into Spinal Dorsal Horn Circuit Function and Dysfunction Using Optical Approaches
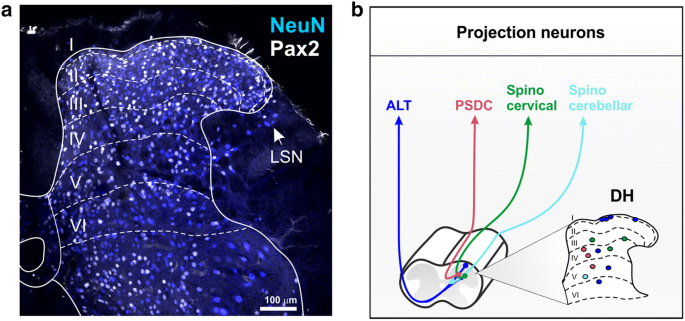
Recent advances in our understanding of the organization of dorsal horn neuron populations and their contribution to cutaneous mechanical allodynia | SpringerLink

Neuronal calcium-binding proteins 1/2 localize to dorsal root ganglia and excitatory spinal neurons and are regulated by nerve injury | PNAS
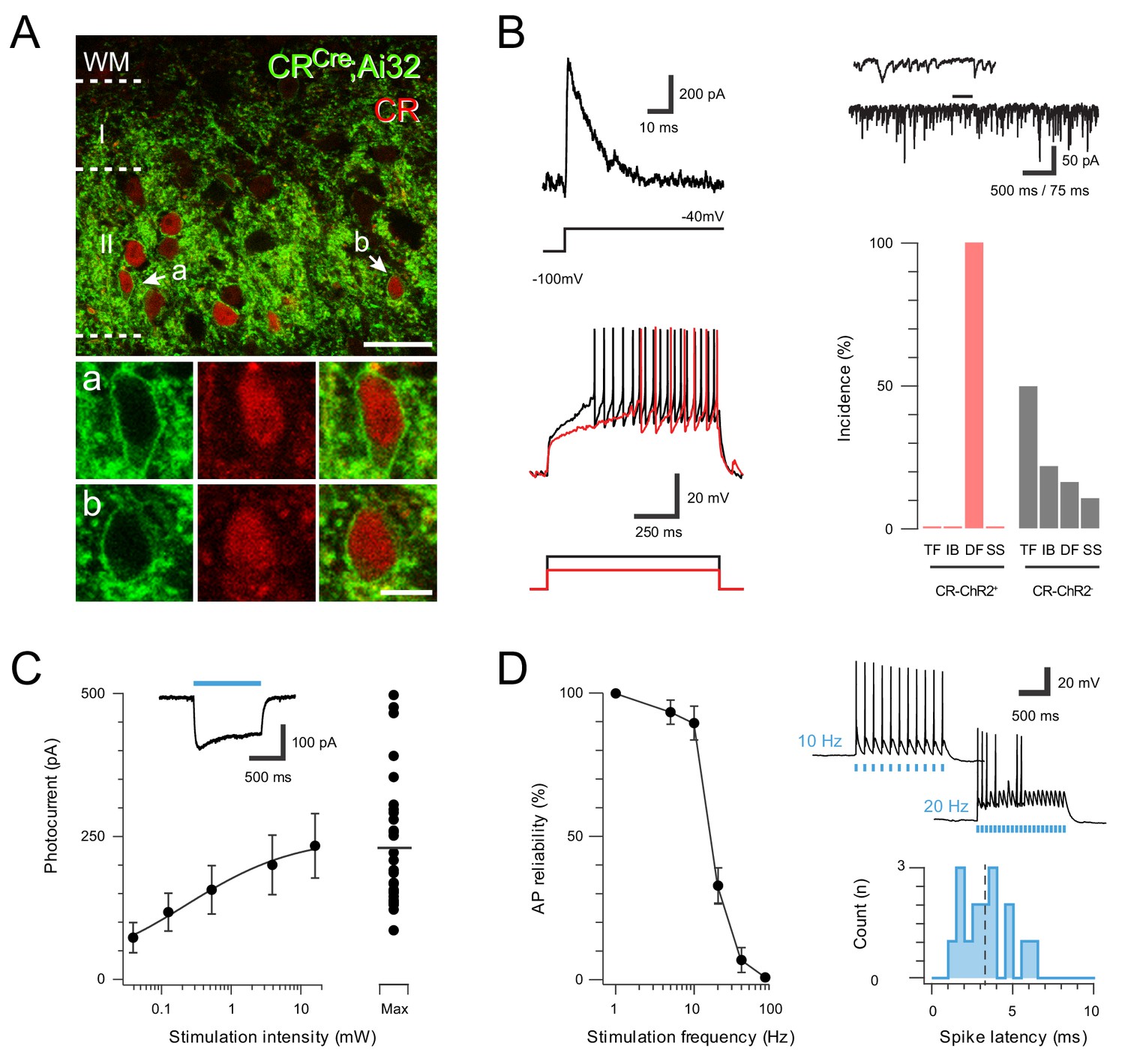
Calretinin positive neurons form an excitatory amplifier network in the spinal cord dorsal horn | eLife
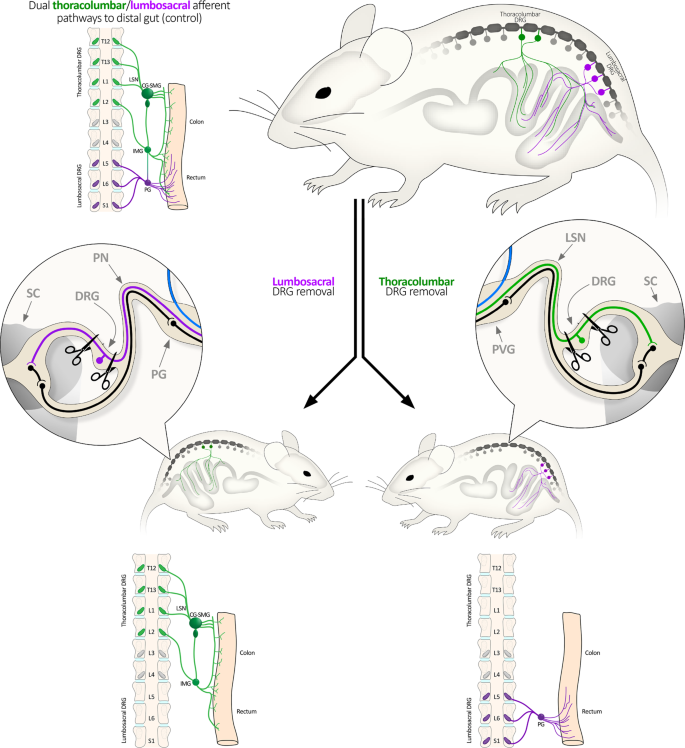
Disengaging spinal afferent nerve communication with the brain in live mice | Communications Biology
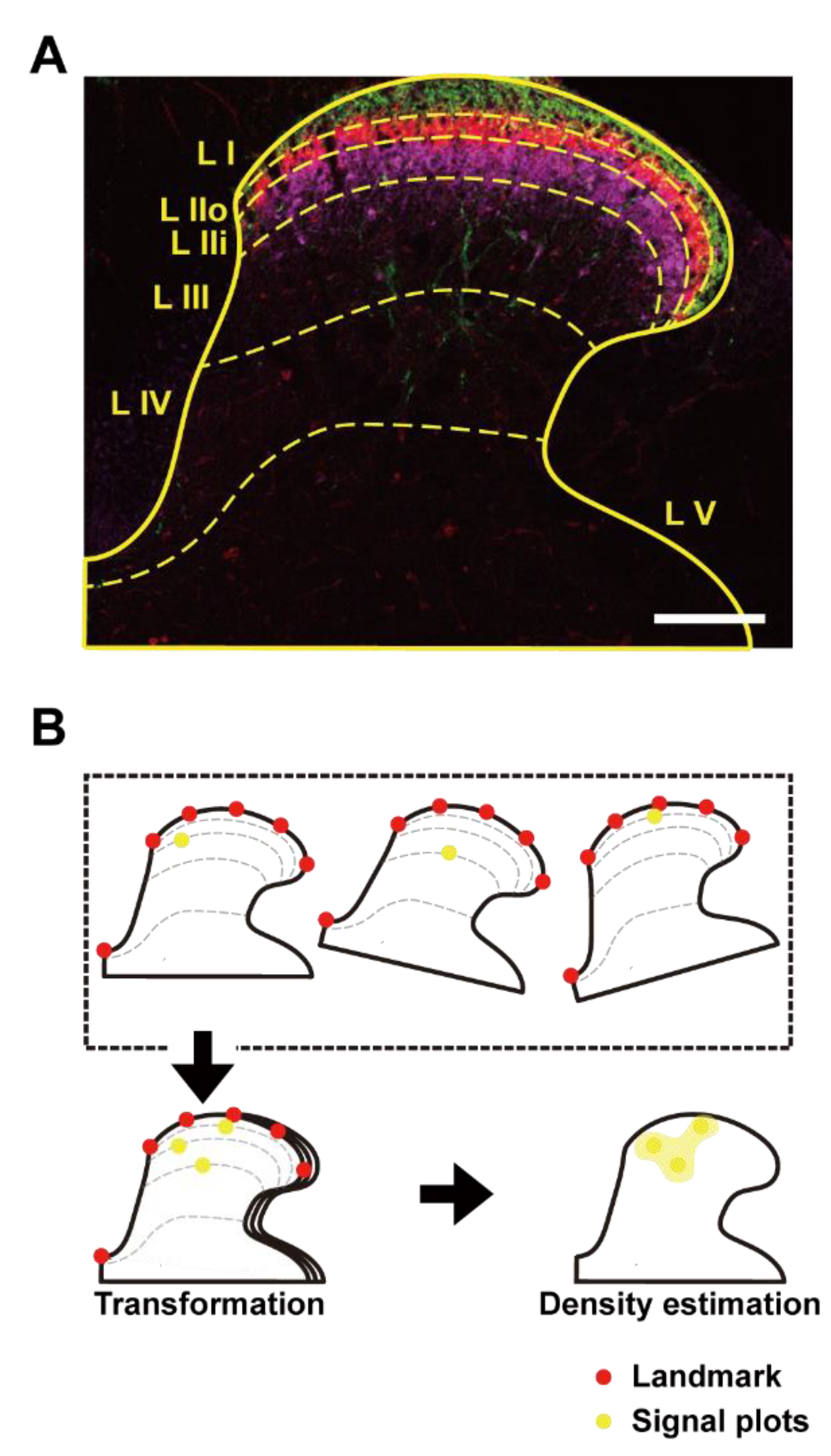
Cells | Free Full-Text | Pre-Synaptic GABAA in NaV1.8+ Primary Afferents Is Required for the Development of Punctate but Not Dynamic Mechanical Allodynia following CFA Inflammation | HTML

Modular Organization of Excitatory Circuits between Neurons of the Spinal Superficial Dorsal Horn (Laminae I and II) | Journal of Neuroscience
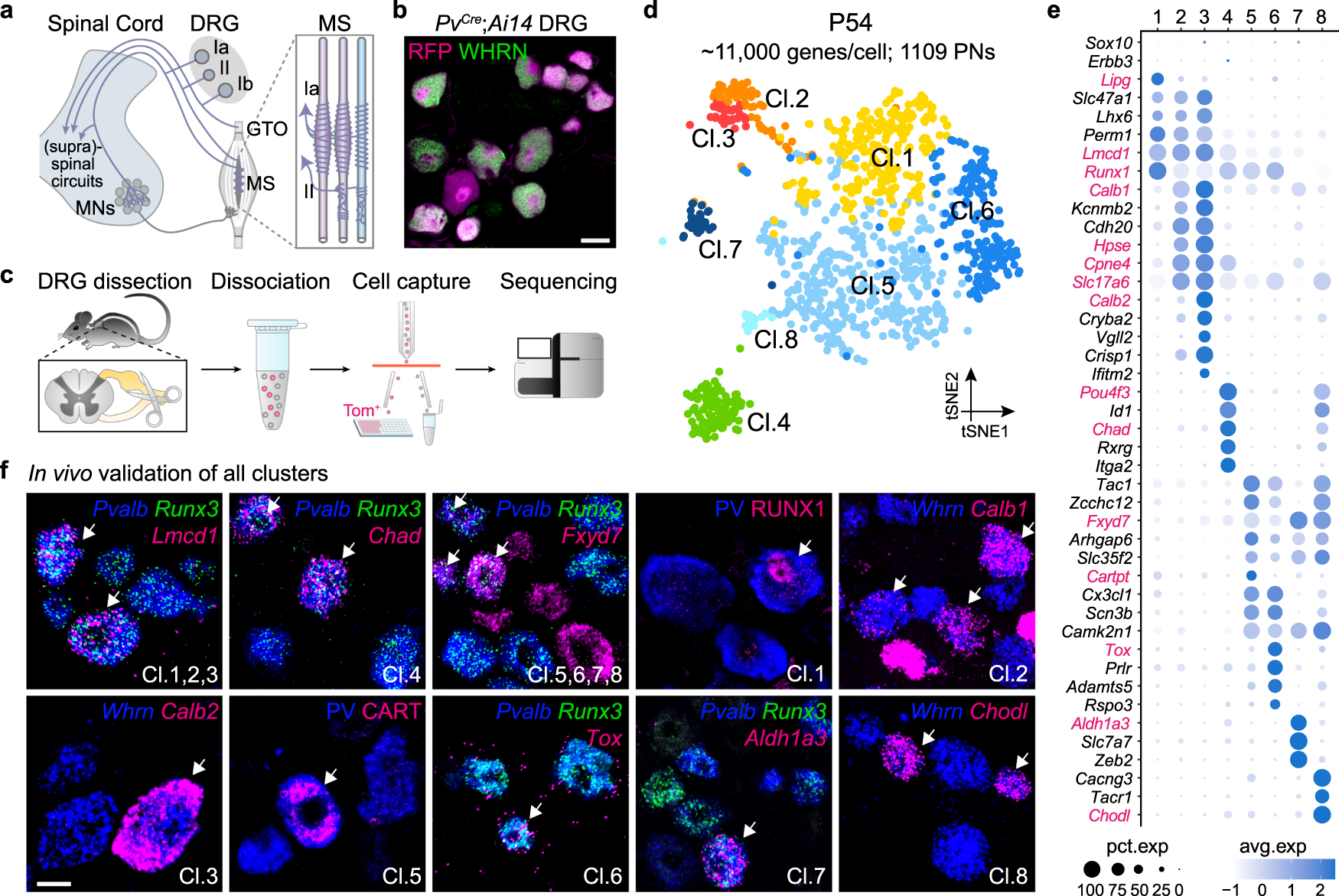
Distinct subtypes of proprioceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons regulate adaptive proprioception in mice | Nature Communications

Transmitting pain and itch messages: a contemporary view of the spinal cord circuits that generate gate control. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Estrogen receptor β is essential for sprouting of nociceptive primary afferents and for morphogenesis and maintenance of the dorsal horn interneurons | PNAS