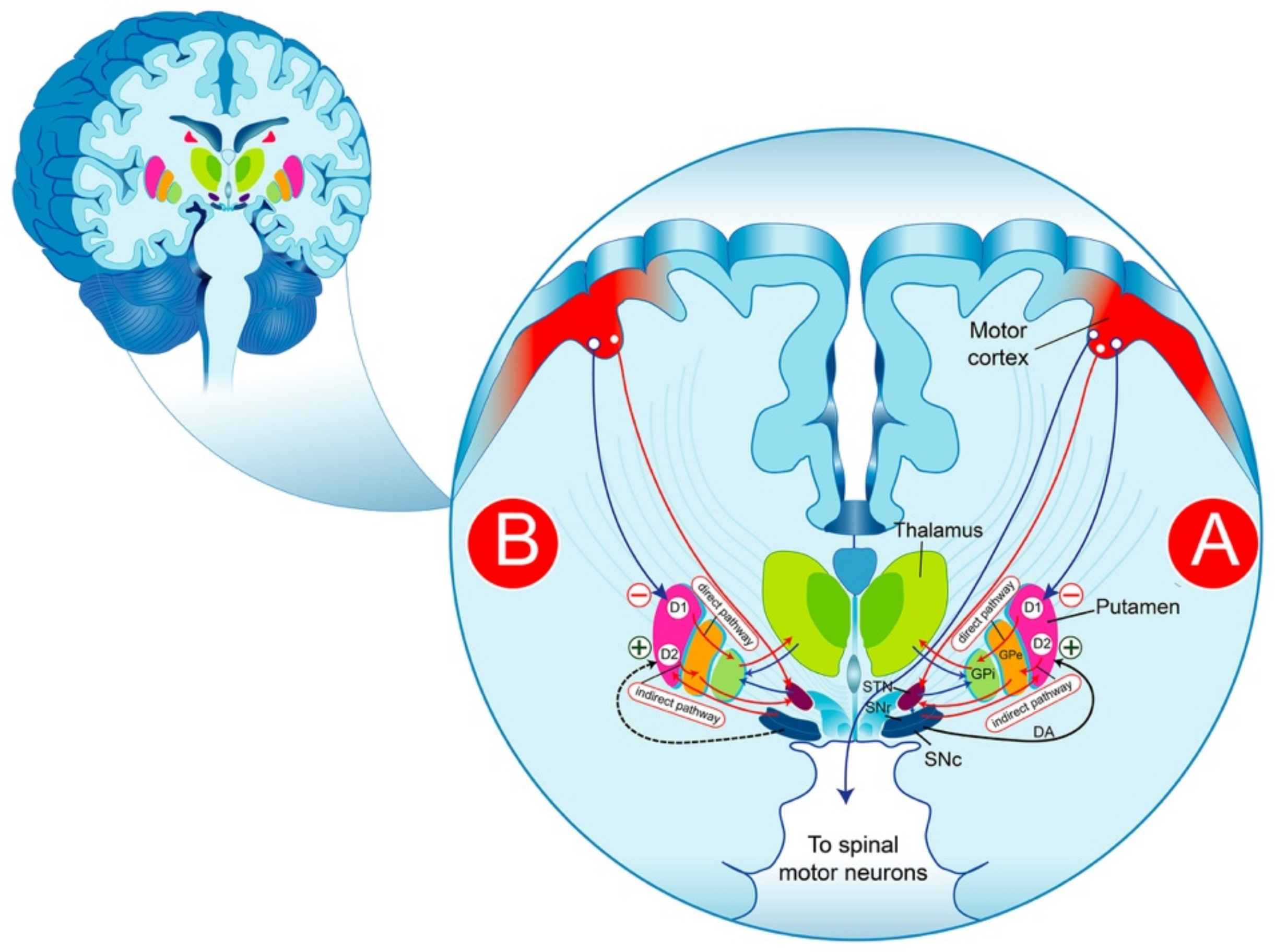
Concomitant shortâ•' and longâ•'duration response to levodopa in the 6â•'OHDAâ•'lesioned rat: a behavioural

Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in patients with Parkinson's disease: filling the bench-to-bedside gap - ScienceDirect

Activation of PPAR gamma receptors reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesias in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in patients with Parkinson's disease: filling the bench-to-bedside gap - ScienceDirect
Imaging Mass Spectrometry Reveals Elevated Nigral Levels of Dynorphin Neuropeptides in L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease | PLOS ONE
Imaging Mass Spectrometry Reveals Elevated Nigral Levels of Dynorphin Neuropeptides in L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease | PLOS ONE

Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in patients with Parkinson's disease: filling the bench-to-bedside gap - The Lancet Neurology
Imaging Mass Spectrometry Reveals Elevated Nigral Levels of Dynorphin Neuropeptides in L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease | PLOS ONE

l-DOPA-induced Dyskinesia is Associated with Regional Increase of Striatal Dynorphin Peptides as Elucidated by Imaging Mass Spectrometry - ScienceDirect

µ Opioid Receptor Agonism for L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson's Disease | Journal of Neuroscience

Enkephalin and dynorphin neuropeptides are differently correlated with locomotor hypersensitivity and levodopa-induced dyskinesia in parkinsonian rats - ScienceDirect

Parkinson's disease: Levodopa‐induced dyskinesia and signal transduction - Santini - 2008 - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library

µ Opioid Receptor Agonism for L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson's Disease | Journal of Neuroscience

Concomitant short‐ and long‐duration response to levodopa in the 6‐OHDA‐lesioned rat: a behavioural and molecular study - Marin - 2007 - European Journal of Neuroscience - Wiley Online Library
Imaging Mass Spectrometry Reveals Elevated Nigral Levels of Dynorphin Neuropeptides in L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease | PLOS ONE
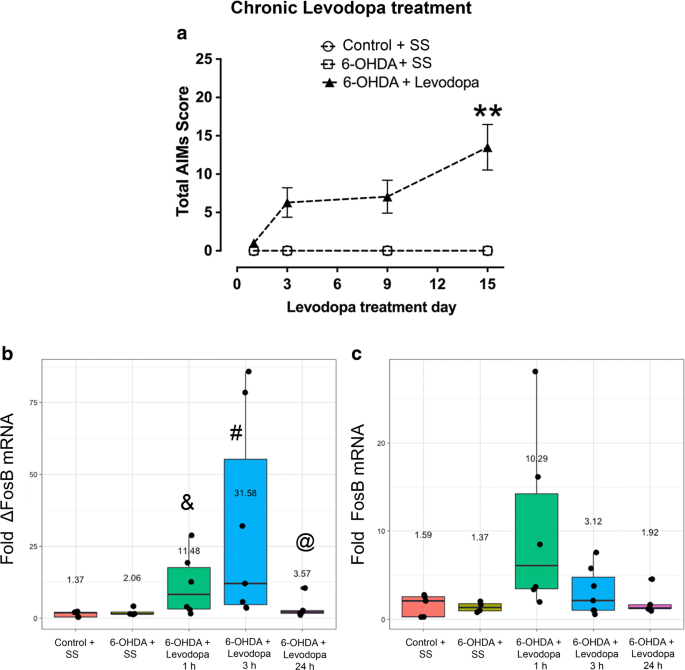
Differential Expression of Striatal ΔFosB mRNA and FosB mRNA After Different Levodopa Treatment Regimens in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease | SpringerLink

Induction of dopamine D3 receptor expression as a mechanism of behavioral sensitization to levodopa | PNAS